The Role of a Galvanometer Scanner in Improving Data Procurement Efficiency
Galvanometer scanners offer as critical components in the world of data purchase, particularly due to their capacity to achieve quick and exact positioning of reflective elements. The implications of their integration expand past mere efficiency; they invite a closer examination of their functional devices and the future developments that may further change information procurement methods.
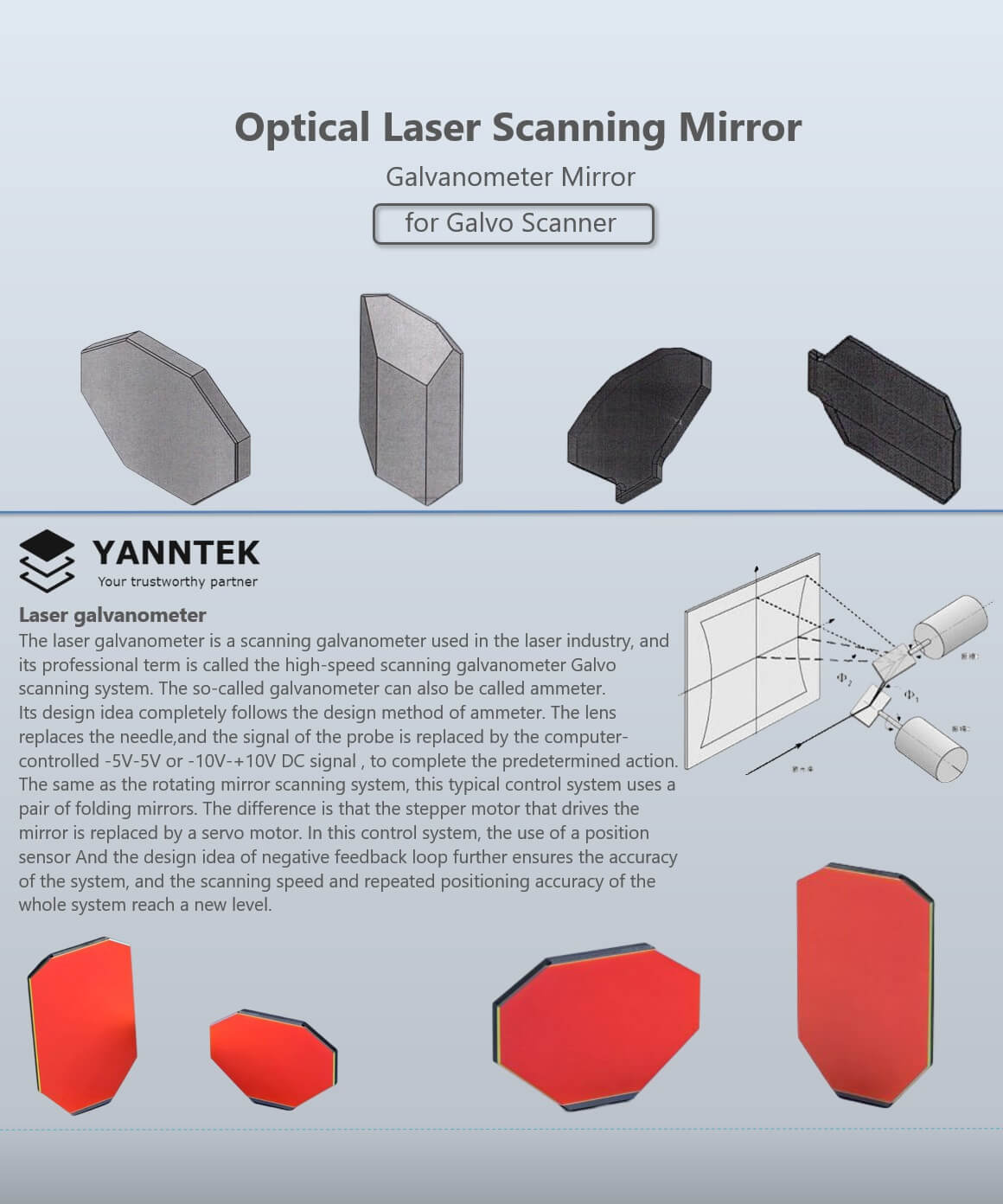
Recognizing Galvanometer Scanners
Using precise electromagnetic principles, galvanometer scanners work as crucial devices in data acquisition systems, making it possible for the precise dimension and recording of electrical signals. These gadgets are designed to transform electric signals into mechanical motion, which can after that be visualized or tape-recorded. The essential characteristic of a galvanometer scanner is its capability to react to variations in current, allowing it to spot minute changes in electric signals with high sensitivity.
Galvanometer scanners are pivotal in a range of applications, consisting of biomedical research study, optical scanning, and quality assurance processes in manufacturing. Their capacity to provide trustworthy and quick analyses makes them ideal for atmospheres that require high accuracy and quick response times. Additionally, the construction of galvanometer scanners usually consists of a light-weight coil put on hold in a magnetic area, allowing them to accomplish high angular deflection with very little inertia.
The flexibility of galvanometer scanners permits for assimilation into many information acquisition systems, enhancing the overall efficiency of signal measurement. By making sure immediate and exact readings, these tools dramatically contribute to the dependability of information evaluation, which is important in both scientific study and commercial applications.
System of Operation
The procedure of a galvanometer scanner depends on the interaction in between electrical currents and electromagnetic fields to produce mechanical movement (galvanometer scanner). At its core, the device contains a coil put on hold within a magnetic field. When an electrical present go through the coil, it creates an electromagnetic field that interacts with the exterior magnetic field, causing torque that causes the coil to revolve. This rotation is commonly gauged in degrees, permitting specific angular variation.
The input current's variant directly influences the angle of deflection, making it possible for the scanner to respond accurately to changes in the input signal. By controling the current's intensity and direction, the galvanometer scanner can achieve quick and exact positioning of a reflective element, such as a mirror. This capacity is essential in applications needing exact positioning and scanning, as it helps with the regulated motion of beams or other signals.
The responses mechanism integrated within many galvanometer scanners additionally boosts their accuracy. Sensing units monitor the placement of the coil, supplying real-time information that can be utilized to readjust the present dynamically. This closed-loop control system makes certain that the scanner keeps precision throughout its operational variety.

Applications in Numerous Industries
Galvanometer scanners discover substantial applications throughout numerous industries because of their precision and fast feedback abilities. In the area of telecommunications, they are integral to laser beam guiding for optical networking, making it possible for high-speed data transmission. Medical diagnostics also benefit significantly from galvanometer scanners, as they are used in laser-based imaging systems, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), offering high-resolution pictures for much better diagnosis.
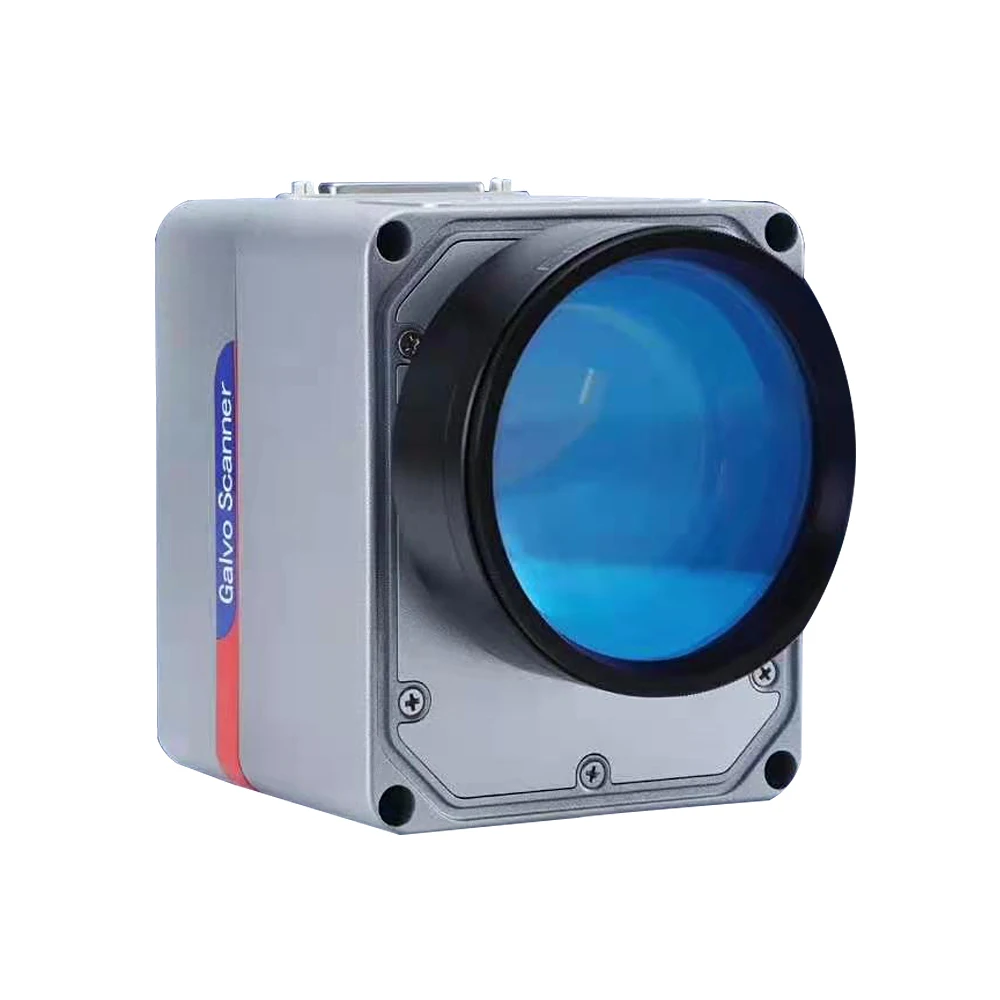

In addition, he said in clinical study, galvanometer scanners are essential for laser scanning microscopy, permitting scientists to capture comprehensive pictures of biological specimens and products. They are also used in metrology for high-precision measurements, making certain compliance with strict industry requirements. On the whole, the adaptability and efficiency of galvanometer scanners make them important across varied industries, considerably adding to advancements in innovation and quality control.
Advantages for Data Procurement
In data acquisition procedures, the unification of galvanometer scanners considerably improves measurement accuracy and speed. These devices utilize high-precision mirrors and rapid angular motions to guide laser beam of lights or lights with remarkable accuracy, which is critical for applications requiring specific positioning and timing.
The flexibility of galvanometer scanners enables seamless assimilation into various data purchase systems, adjusting to particular requirements in fields such as biomedical imaging, products testing, and ecological surveillance. This versatility not only improves the convenience of the tools but also optimizes the overall effectiveness of data collection workflows.
Furthermore, the small design of galvanometer scanners facilitates very easy installment and maintenance, additional adding to functional performance. Eventually, the advantages of employing galvanometer scanners in data procurement processes convert to far better top quality data, lowered operational costs, and improved job turnaround times.
Future Trends and Innovations
Improvements in modern technology are positioned to drive the evolution of galvanometer scanners, further improving their role in information procurement. Emerging innovations are likely to concentrate on increasing scanning rates and enhancing accuracy, enabling for more reliable information collection in applications ranging from biomedical imaging to commercial automation.
Integration of man-made knowledge and maker learning formulas is anticipated to play a crucial duty in optimizing scanner efficiency. These innovations can enable real-time changes during the scanning procedure, enhancing precision and see post decreasing mistakes. The incorporation of advanced materials, such as lightweight compounds, can lead to the development of even more nimble scanners with enhanced responsiveness.
Additionally, the pattern towards miniaturization will likely lead to portable galvanometer systems, making them more available for numerous applications, consisting of mobile devices. Enhanced connection via IoT integration can assist in seamless data transfer and remote monitoring, more streamlining information procurement processes.
As the demand for high-resolution imaging and rapid data processing continues to expand, galvanometer scanners will certainly advance to satisfy these requirements, placing themselves as important devices in the quest for efficiency throughout several fields. The future assures Read Full Report a transformative journey for galvanometer modern technology, driven by advancement and precision.
Conclusion
In final thought, galvanometer scanners considerably enhance information purchase efficiency via their fast and accurate placing abilities. As industries proceed to integrate these scanners into their systems, ongoing advancements and fads are anticipated to further maximize their performance, strengthening their necessary function in the development of data acquisition innovations.
Galvanometer scanners offer as critical parts in the realm of data purchase, specifically due to their capability to accomplish rapid and accurate positioning of reflective aspects.Utilizing specific electromagnetic concepts, galvanometer scanners serve as necessary devices in information procurement systems, making it possible for the exact dimension and recording of electrical signals. On the whole, the flexibility and efficiency of galvanometer scanners make them crucial throughout varied fields, substantially contributing to innovations in technology and top quality assurance.
One of the primary advantages of galvanometer scanners is their capability to achieve high-speed data collection.In conclusion, galvanometer scanners significantly enhance data purchase efficiency via their specific and rapid placing abilities.
Comments on “Cutting-edge Uses of a Galvanometer Scanner in Industrial Automation and Control”